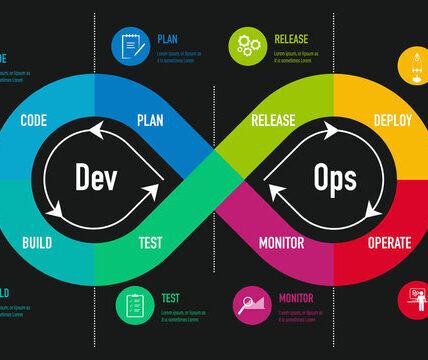
In the fast-paced world of software development, efficiency and automation are key. This is where Jenkins, an open-source automation server, enters the scene. It helps you streamline your software development life cycle (SDLC) by automating various tasks, including:
- Building and testing your code: No more manual builds and test runs. Jenkins automatically triggers them after every code change, ensuring consistency and quality.
- Deploying your application: Automatically deploy your builds to different environments (development, testing, production), saving you time and effort.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Integrate and test code changes frequently, catching bugs early and preventing regressions.
- Continuous Delivery (CD): Deliver new features and updates faster with confidence, thanks to automated testing and deployment.
If you want to improve your development workflow and release cycle, Jenkins is a valuable tool. Now, let’s dive into the practical aspects:
Installing Jenkins on Linux: A Step-by-Step Guide
There are several ways to install Jenkins on Linux, but we’ll focus on the two most common methods:
1. Using a Package Manager:
- Ubuntu/Debian:
Bash
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
Use code with caution.content_copy
- Red Hat/CentOS:
Bash
sudo yum install java-11-openjdk -y
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo
sudo yum install jenkins -yUse code with caution.content_copy
2. Downloading the WAR file:
- Download the latest WAR file from https://jenkins.io/download/.
- Start a servlet container like Tomcat and deploy the WAR file.
- Configure port and other settings based on your needs.
4. Starting and Accessing Jenkins:
Once the installation is complete, start the Jenkins service:
- Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo systemctl start jenkins - Red Hat/CentOS:
sudo systemctl start jenkins
Access the Jenkins web interface by opening http://localhost:8080 (or the port you configured) in your browser.
5. Initial Setup:
Upon first access, you’ll need to unlock Jenkins using a randomly generated password found in the /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword file. Follow the on-screen instructions to set up an admin user and install essential plugins.
Deploying Jenkins with Docker Compose: A Streamlined Setup
In addition to traditional installation methods, you can leverage Docker Compose to easily deploy and manage Jenkins within a containerized environment. Here’s a guide to get you started:
1. Create a docker-compose.yml file:
version: "3.8"
services:
jenkins:
image: jenkins/jenkins:lts
ports:
- "8080:8080" # Expose Jenkins web interface
- "50000:50000" # Optional: Expose JNLP slave agent port
volumes:
- jenkins_home:/var/lib/jenkins:rw
- docker-socket:/var/run/docker.sock:ro # Optional: Grant access to Docker daemon
environment:
- INITIAL_ADMIN_PASSWORD=your_password
volumes:
jenkins_home:
docker-socket:
Explanation:
- We define a
jenkinsservice that uses the official Jenkins image. - Ports are mapped to expose the web interface and optional JNLP slave agent communication.
- A volume named
jenkins_homepersists data (plugins, configurations) outside the container. docker-socketvolume (optional) grants Jenkins access to the Docker daemon for managing containerized builds.- The environment variable
INITIAL_ADMIN_PASSWORDsets the initial administrator password. - Separate volumes are defined for
jenkins_homeanddocker-socket(if used).
2. Start the deployment:
Bash
docker-compose up -dThis command builds and starts Jenkins in a detached mode, running in the background.
3. Access Jenkins Web Interface:
Open http://localhost:8080 in your browser and use the initial password set in the environment variable to log in.
4. Customize and extend:
- Install plugins within the web interface to suit your workflow.
- Configure Jenkins jobs and pipelines to automate your building, testing, and deployment processes.
Remember:
- This is a basic example. You can customize the configuration based on your specific needs.
- Secure your deployments by implementing proper network segmentation and authentication mechanisms.
- Consider leveraging additional Docker Compose features like environment variables, secrets, and scaling options for a more robust setup.
Now you’re ready to explore the world of Jenkins and unleash its automation power!
Additional Resources:
- Jenkins documentation: https://jenkins.io/doc/
- Tutorials and guides: https://jenkins.io/doc/tutorials/
- Community forum: https://community.jenkins.io/
Remember, this is just a starting point. As you delve deeper into Jenkins, you’ll discover a vast array of features and plugins to customize your CI/CD pipeline and unlock the full potential of automated software development. Happy automating!